Objective 7
Problem Solving with Various Mathematical Tools
Theorems and Properties
Features:
- Fundamental laws such as commutative, associative, and distributive.
- Identity, dominance, absorption theorems, etc.
Gates:
- Representation of logical functions using AND, OR, NOT gates.
- Implementation in electronic circuits.
Principles of Duality:
- Relationship between dual operations like AND and OR, 1 and 0.
- Allows simplification of logical expressions by swapping operators and variables.
Combinatorial Circuits
Features:
- Design of circuits where the output depends solely on the current inputs.
- Examples include adders, decoders, multiplexers.
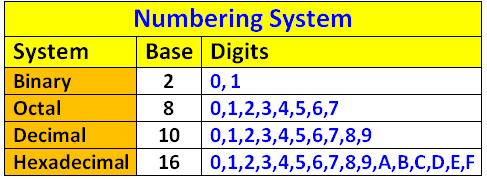
Numeric Systems
Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal:
- Representation of numbers in different numerical bases.
- Conversion between numerical bases and its significance in computing.
Numeric Representation:
- Meaning of bits and their representation in numerical systems.
- Importance of Most Significant Bit (MSB) and Least Significant Bit (LSB).
Base Conversion:
- Procedures for converting numbers between bases, such as the method of successive division.
Basic Operations and Matrix Theorems
Basic Operations:
- Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division in different numerical bases.
- Application of algebraic laws in expression simplification.
Matrices and Matrix Algebra:
- Matrix operations such as addition, multiplication, inversion.
- Applications in systems of linear equations and linear transformations.
Recurrence Relations and Classical Problems
Recurrence Relations:
- Expressions that relate a term to previous terms in a sequence.
- Examples include the Fibonacci sequence and the Towers of Hanoi problem.
Fibonacci Sequence:
- Recursive definition and its relationship with the golden ratio.
- Applications in computer science, mathematics, and nature.
Towers of Hanoi:
- Description of the problem and its recursive solution.
- Examples of algorithmic implementations.
Ackermann Function
Ackermann Function:
- Mathematical definition of a recursively increasing function.
- Description of its properties and applications in theoretical computer science.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario